Solar energy (solar energy) refers to the thermal radiation energy of the sun (see the three ways of thermal energy transmission: radiation), the main performance is often said that the sun’s rays. Although the energy radiated by the sun to the earth’s atmosphere is only 1/2.2 billion of its total radiant energy, it is as high as 173,000 TW, which means that the energy that the sun irradiates on the earth every second is equivalent to 5 million tons of coal. The energy hitting the earth is 499,400,00,000 joules. Solar energy in a broad sense is the source of many energy on earth, such as wind energy, chemical energy, potential energy of water and so on. Fossil fuels can be considered ancient solar energy. In a narrow sense, solar technology is characterized as passive or active ways to capture, convert and distribute sunlight. Passive solar technology, mainly used in infrastructure construction and other fields, includes selecting materials with good thermal properties, designing spaces for natural air circulation, and arranging the location of buildings in accordance with the sun. Active solar technology directly converts sunlight into other forms of energy as energy output.
Here we will limit our discussion to active (active) solar technology, a type of energy that can be generated. There are two common forms, one is Photovoltaics (PV) and the other is Solar Thermal Energy (STE).
1) Solar photovoltaic
Solar photovoltaic, referred to as photovoltaic (Photovoltaics; word source “photo-” light, “voltaics” volt), refers to the use of photovoltaic semiconductor materials photovoltaic effect, and the solar energy is converted into direct current electricity facilities. Specifically, the photovoltaic effect refers to the phenomenon in which light produces a potential difference between different parts of a semiconductor or a combination of semiconductors and metals.
The type of solar cells can be divided into substrate type and thin film type, and the substrate type can be divided into single crystal type or polycrystalline type substrate after being dissolved and cooled; the thin film type can be compared with buildings. It has the characteristics of curvature, flexibility, foldability, etc., and amorphous silicon is more commonly used as a material. In addition to the first two, there are other solar cells made of organic or nanomaterials, which are still in the research and development stage.
Solar cells are divided into silicon-based semiconductor cells, CdTe thin film cells, CIGS thin film cells, dye-sensitized thin film cells, and organic material cells according to their production materials. Among them, silicon cells are further divided into monocrystalline cells, polycrystalline cells and amorphous silicon thin film cells. The most important parameter for solar cells is conversion efficiency. Among the silicon-based solar cells developed in the laboratory, the efficiency of monocrystalline silicon cells is 25.0%, the efficiency of polycrystalline silicon cells is 20.4%, and the efficiency of CIGS thin film cells is 19.8%. The efficiency of CdTe thin film cells is 19.6%, and the efficiency of amorphous silicon (amorphous silicon) thin film cells is 10.1%. (Solar cell efficiency tables )

It is worth noting that a certain battery manufacturing technology can not only manufacture one type of battery. For example, in the polysilicon process, both the silicon crystal plate type and the thin film type can be manufactured. Its design mainly uses different processes and methods to test the reaction and absorption of light, so as to achieve a revolutionary breakthrough in combining a wide energia gap, so that both short wavelengths and long wavelengths can be fully absorbed, so as to reduce the cost of materials.
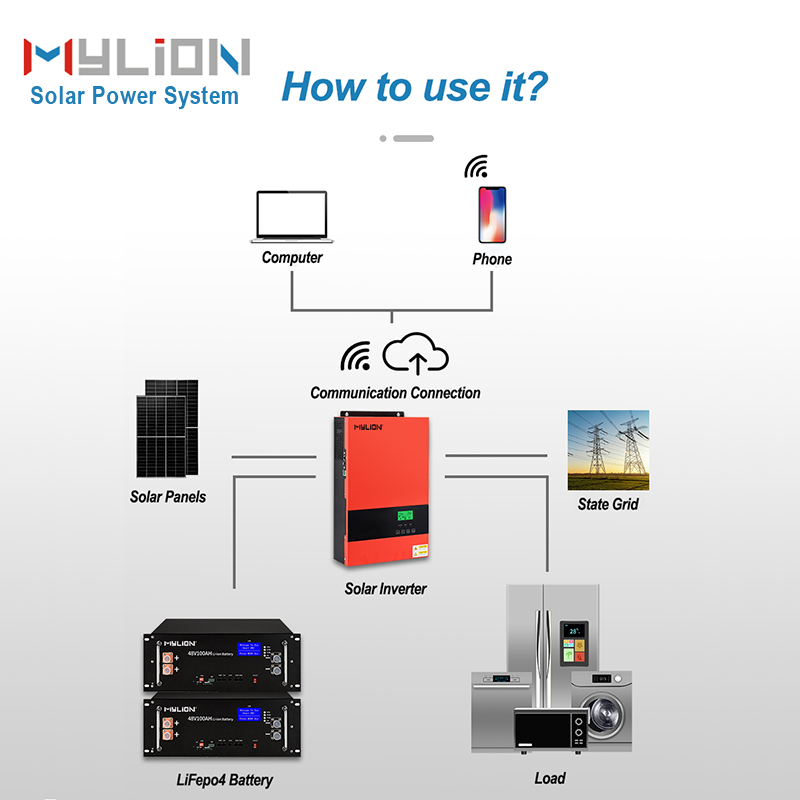
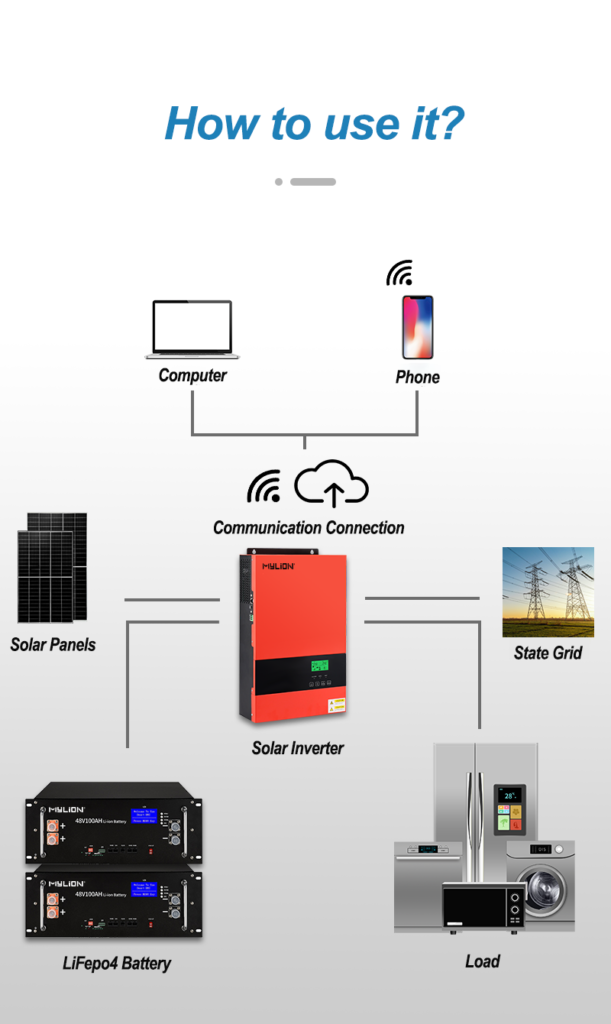
Since the electricity generated by solar cells is direct current, if you need to provide power to household appliances or various electrical appliances, you need to install a direct/AC converter and replace it with alternating current, so that it can supply electricity for household or industrial use.
There are two types of solar power plants: independent operation and grid-connected operation.
At the same time, the classification of solar photovoltaic power generation systems, one is centralized, such as large-scale northwest ground photovoltaic power generation systems; the other is distributed (with >6MW as the boundary), such as industrial and commercial enterprise plant rooftop photovoltaic power generation systems, residential rooftop photovoltaic power generation systems.
2) Solar thermal energy
Solar thermal energy is a thermal energy (heat) technology that utilizes solar energy, mainly by receiving or concentrating solar radiation and converting it into thermal energy for use. Modern solar technology can combine sunlight and use its energy to generate hot water, steam and electricity.
The U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) classifies solar collectors as low, medium, and high temperature collectors. Plates of low temperature collectors are generally used to heat swimming pools. Medium temperature collectors are also usually flat plates, but are used to make hot water or space heating for both residential and commercial purposes. High-temperature collectors use mirrors or lenses to collect sunlight, and are generally used to produce electricity, which is often referred to as concentrated solar power generation.
Concentrated solar thermal power generation (or called concentrated solar thermal power generation, English: Concentrated solar power, abbreviation: CSP) is a power generation system of a concentrating solar power plant. It uses mirrors or lenses, and uses optical principles to gather a large area of sunlight into a relatively small light-collecting area, so that the solar energy is concentrated. The light-collecting area on the generator is illuminated by sunlight and the temperature rises. Converts solar energy into heat energy, which is powered by a heat engine (usually a steam turbine engine) to drive a generator, thereby producing electricity.
At present, there are mainly three types of concentrated solar thermal power generation systems:
The main components of the dish solar concentrating power generation system include solar concentrators and energy converters. The solar concentrator dish-like structure can continuously track the sun to collect energy from the sun and focus it on a small area. In order to save costs, many small flat mirrors are often used to form a dish-like structure. The energy converter consists of two parts, the thermal energy receiver and the engine/generator. A thermal receiver absorbs the energy from the focused sunlight, converts it into heat, stores it in hot air or hot water, and delivers the heat to a heat engine, often a Stirling engine, that converts the heat Converted into mechanical energy to drive the power generation device.
CSP systems utilize an entire array of sun-tracking mirrors (heliostats) to concentrate sunlight onto a central receiver. This receiver is fixed on top of a tower. The heat transfer fluid inside the receiver can be used to generate steam to power a conventional turbine generator to generate electricity. Developed in the 1980s, the tower-type solar thermal power generation system uses steam as the heat transfer fluid. The new system uses molten nitrate as the heat transfer fluid, mainly because of the fluid’s superior heat capacity and heat transfer capabilities.
The trough concentrator power generation system adopts a rectangular reflector bent into a U-shaped groove. The angle of the mirror is adjusted to focus the sunlight, and it is irradiated on the receiving tube of the same length parallel to the groove. The fluid in the glass tube is heated by the heating oil. , which produces steam, which in turn drives a turbine to generate electricity. There are two main types of trough concentrating power generation systems, one is a parabolic shape, the receiving tube is placed on the focal line; the other is a Fresnel reflection system, a receiving tube is placed on multiple mirrors so that the mirrors are placed on the focal line. More flexibility when tracking the sun.

3) Comparison of solar photovoltaic power generation and concentrated solar power generation
Solar photovoltaic power generation: simple structure is conducive to distributed applications, but the conversion rate is low
Concentrated solar power generation: high conversion efficiency, mature technology, good stability, low cost, but large volume and complex structure.