Current mobile electronic devices are largely separated from chemical batteries, which are devices that convert chemical energy into electrical energy. At present, batteries are accustomed to, but for the human beings in the 18th century, it was incredible. As a magical pen in the early 19th century, how was the battery recognized by humans? Why do lithium batteries dominate the consumer electronics industry.
Volta battery born on frog’s thigh
When it comes to chemical batteries, there is indeed an indispensable name, that is Volta, and his name is forever engraved in human textbooks. Volta had an old friend, Galvani, who was a professor of crack science. At that time, Galvani discovered a peculiar biological phenomenon: placing the legs of a newly dead frog on a copper plate and clipping the frog’s thigh with a clip, the muscles of the thigh would twitch. As it happens, this clip is made of metal zinc. Galvani believed that the body fluids in the frog’s thighs contained animal electricity, and when the metal came into contact, it was a discharge process. When Volta heard this, he held the opposite opinion. Volt believed that there was no bio-electricity in animal body fluids, and that the current came from the contact of two different metals with the body fluid. Two old friends hold their own opinions.

Volta eventually proved his idea with an invention, the Volt heap, one of the objects at the back of the photo above.
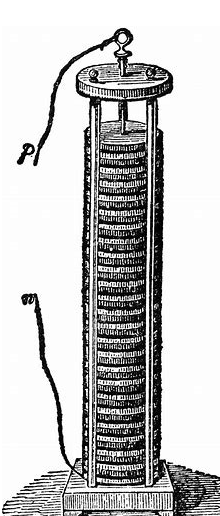
The process of volt proof is very simple and classic, that is, replace frog thighs with cardboard soaked with salt water, first use zinc and silver as metal at both ends, and then lead out silver and zinc metal as wires, when the outgoing power lines are connected , is to generate current. Moreover, the battery made in the form of this volt stack has a relatively stable voltage and stores a lot of electricity. This is the first battery in human history.
In 1800, Volta recorded the method and process of making it in detail and shared it with everyone. Napoleon was also very interested after hearing about it, and invited Volta to explain his invention.
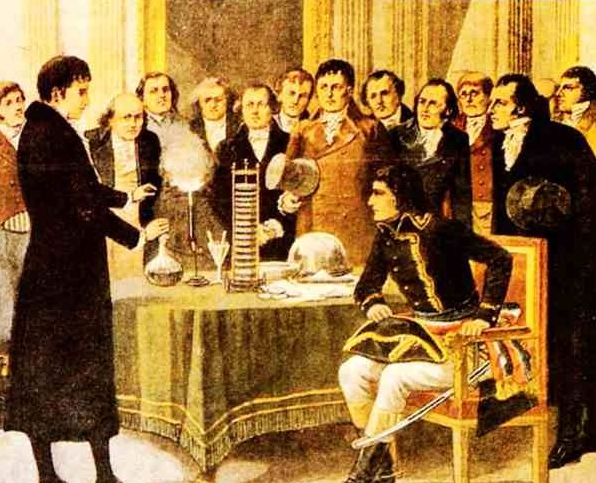

On the display, Volta wanted to show Napoleon that the volta pile could burn the iron wire red, making the water bubble, and Napoleon also personally experienced the feeling of an electric shock.
According to the classification of modern science, the volt stack belongs to the primary battery, that is, the battery that cannot be used repeatedly.
Dry batteries
The metal lithium primary battery we are more familiar with is the button battery that is often used in watches and calculators. It is a typical lithium primary battery.

Zinc-manganese dry battery is a barrel dry battery commonly used in daily life.

Note that the lithium battery here refers to a primary dry battery. The lithium battery in the table is a primary lithium battery that uses metal Li as the negative electrode and SOCl2 as the positive electrode. The lithium battery we often say refers to the rechargeable lithium battery.
This involves the second category of batteries, secondary batteries.
The first rechargeable battery in the world
In 1859, the Frenchman Plante discovered that when direct current passed through two lead plates immersed in dilute sulfuric acid, electromotive force could be repeatedly generated on the two lead plates, thus making a lead-acid battery. This kind of battery not only has high energy storage density, but also can be used many times by charging. This is the first rechargeable battery in human history: the lead-acid battery. Lead acid batteries are available in 2.4V, 4V, 6V, 8V, 12V, 24V series with capacities from 200mAh to 3000Ah.

At present, it is very common for electric vehicles to still use lead-acid batteries.
Subsequently developed nickel-cadmium batteries, nickel-metal hydride batteries.
Nickel-cadmium batteries
The positive electrode material of the nickel-cadmium battery is composed of nickel oxide powder and graphite powder; the negative electrode material is composed of cadmium oxide powder and iron oxide powder. Nickel-cadmium battery is the earliest type of battery used in mobile phones. It can be repeatedly charged and discharged for more than 500 times. It is economical and durable. It can provide large current for the load, and the voltage change during discharge is small. It is a very ideal DC power supply battery.
The most fatal disadvantage of nickel-cadmium batteries is that if they are not handled properly during the charging and discharging process, there will be a serious “memory effect”, which will greatly shorten the service life. The so-called “memory effect” means that the battery’s power is not completely discharged before the battery is charged, which will cause the battery capacity to decrease over time. In addition, cadmium is toxic and will cause heavy metal pollution, so nickel-cadmium batteries are not conducive to the protection of the ecological environment. These shortcomings make nickel-cadmium batteries basically out of the scope of application of digital equipment batteries.
Ni-MH battery (Ni/MH)
It is a modification of nickel-cadmium batteries, which replace cadmium (Cd) with a metal that can absorb hydrogen. The birth of nickel-metal hydride batteries is attributed to the discovery of hydrogen storage alloys. Hydrogen storage alloys can absorb and release a large amount of hydrogen under certain temperature and pressure conditions, so they are vividly called “hydrogen-absorbing sponges”. In a strong alkaline electrolyte solution, it is repeatedly charged and discharged and exists stably for a long time, thereby providing a new type of negative electrode material, and on this basis, a nickel-hydrogen battery is invented. The main source of hydrogen storage alloys is rare earth, and China’s rare earth resources account for more than 70% of the world’s total reserves. The development of nickel-metal hydride batteries has unique advantages.
The capacity of existing NiMH batteries is already higher than that of alkaline batteries (by volume). Taking AA batteries as an example, the marked capacity of NiMH batteries can reach 2900mAh, while the capacity of alkaline batteries is only ~2100mAh, which is of course much higher than that of NiCd. The battery’s 1100mAh, but it still falls short of a Li-ion battery.
The disadvantage of NiMH batteries is that they are more expensive than NiCd batteries.

Lithium battery
Lithium batteries are the crown of rechargeable batteries.
Lithium secondary batteries have been very popular in research for a long period of time, but so far, secondary batteries with metal lithium as the negative electrode have not been put into production. Why? The key is safety.
If metallic lithium is used, the discharge process is the same as before, and the charging process is reversed. The external circuit provides a lot of electrons to the negative electrode, and lithium ions obtain electrons at the negative electrode and are precipitated. The problem is that dendrite segregation occurs during the precipitation of metallic lithium, that is A dendrite-like crystal is formed, and when the dendrites are long enough to be connected from the positive electrode to the negative electrode, a short circuit occurs, and the lithium battery will explode.
Therefore, the development of lithium secondary batteries has encountered a huge bottleneck at this time. The researchers had to find a substance that could absorb metallic lithium to prevent dendrite segregation to replace lithium as the negative electrode. This great idea originated from Bell Labs in 1981, and the substance they were looking for was also familiar to us as graphite. As we all know, graphite has a layered structure, so lithium metal is easily inserted into graphite to form a graphite interlayer compound composed of C6Li, which avoids the problem of lithium dendrite segregation during charging, and successfully solves the problem of secondary battery. Safety issues have directly led to the production of lithium-ion batteries.
Advantages of Lithium Batteries
High voltage, the working voltage of the single battery is as high as 3.7-3.8V (3.2V for lithium iron phosphate), which is 3 times that of nickel-cadmium batteries and nickel-hydrogen batteries
Large specific energy, 3-4 times that of Ni-Cd batteries, 2-3 times that of Ni-MH batteries
Long cycle life, generally can reach more than 500 times, even more than 1000 times, lithium iron phosphate can reach more than 2000 times
Good safety performance, does not contain cadmium, lead, mercury and other elements that pollute the environment, no memory effect
These advantages have led to the overwhelming application of lithium batteries. You can see lithium batteries in electric vehicles, electric vehicles, and digital products.

Science and technology benefit mankind. As a relatively ancient industry, the battery industry has created a steady stream of power for a new round of technological innovation due to the emergence of lithium batteries.






