1. Definition of cylindrical battery
Cylindrical lithium batteries are divided into different systems of lithium iron phosphate, lithium cobalt oxide, lithium manganate, cobalt-manganese hybrid, and ternary materials. The outer shell is divided into two types: steel shell and polymer. Batteries with different material systems have different advantages. At present, the cylinders are mainly steel-shell cylindrical lithium iron phosphate batteries, which are characterized by high capacity, high output voltage, good charge and discharge cycle performance, stable output voltage, large current discharge, stable electrochemical performance, and use Safe, wide operating temperature range, environmentally friendly, widely used in solar lamps, lawn lamps, back-up energy, power tools, toy models.
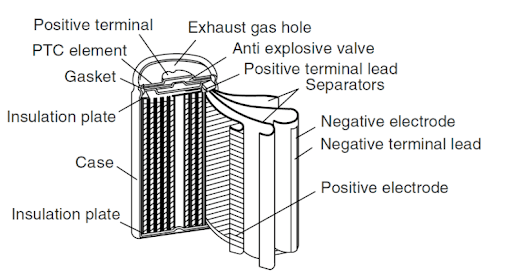
2. Cylindrical battery structure
The structure of a typical cylindrical battery includes: shell, cap, positive electrode, negative electrode, separator, electrolyte, PTC element, gasket, safety valve, etc. Generally, the battery case is the negative electrode of the battery, the cap is the positive electrode of the battery, and the battery case is made of nickel-plated steel plate.
3. The advantages of cylindrical lithium batteries
Compared with soft packs and square lithium batteries, cylindrical lithium batteries have the longest development time, with higher standardization, more mature technology, high yield and low cost.
Mature production technology, low PACK cost, high battery product yield, and good heat dissipation performance
Cylindrical batteries have formed a series of internationally unified standard specifications and models, with mature technology and suitable for continuous mass production.
The cylinder has a large specific surface area and a good heat dissipation effect.
Cylindrical batteries are generally sealed batteries, and there are no maintenance problems during use.
The battery shell has high withstand voltage, and there will be no phenomena such as square or soft-packed battery expansion during use.