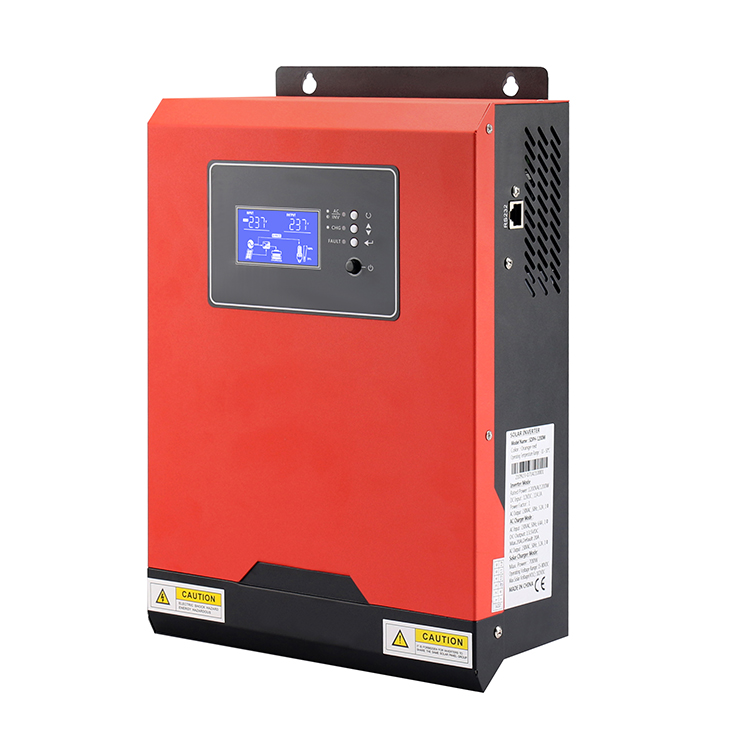
The inverter is a converter that converts DC power (battery, storage battery) into constant frequency and constant voltage or frequency modulation and voltage regulation AC power (usually 220V, 50Hz sine wave). It consists of inverter bridge, control logic and filter circuit. In most cases, the input DC voltage is usually lower, while the output AC voltage is equal to the grid supply voltage of 120v or 240v, depending on the country.
Connecting home appliances to the output of the power converter enables a variety of appliances to be used in the car. Electrical appliances that can be used include: air conditioners, computers, digital cameras, cameras, lighting, fans, CD players, game consoles, PDAs, power tools, car refrigerators and various travel, camping, medical emergency appliances, etc.
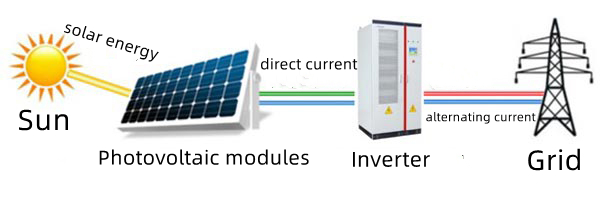
Inverters can be built as stand-alone devices for applications such as solar power, or as a backup power source for separately charged batteries. Another configuration is when it is part of a larger circuit, such as a power supply unit or UPS. In this case, the input DC power to the inverter comes from the rectified mains AC in the PSU, from the rectified AC in the UPS when power is available, and from the battery when the power fails.
Inverters provide AC voltage from a DC power source and can be used to power electronic and electrical equipment rated for the AC power supply voltage. In addition, they are widely used in the inverting stage of switch-mode power supplies. Circuits are classified according to switching technology and switching type, waveform, frequency, and output waveform.
Basic Inverter Operation
The basic circuits include oscillators, control circuits, drive circuits for power devices, switching devices and transformers.
The conversion of DC to AC voltage is accomplished by converting energy stored in a DC power source (such as a battery) or from the output of a rectifier to AC voltage. This is done using a switchgear that turns on and off continuously, and then steps up using a transformer. Although there are some configurations that do not use transformers, these are not widely used.
The DC input voltage is turned on and off by power devices and pulses fed to the primary side of the transformer. The varying voltage in the primary induces an AC voltage at the secondary winding. Transformers can also be used as amplifiers, which increase the output voltage at a ratio determined by the turns ratio. In most cases, the output voltage is boosted from the standard 12v provided by the battery to 120v or 240v AC.
The three commonly used inverter output stages are push-pull, push-pull half-bridge or push-pull full-bridge with a center-tapped transformer. Push-pull with center tap is most popular for its simplicity and guaranteed results; however, it uses a heavier transformer and is less efficient.